SENSE
Smart Grid UC
As a result of the adoption of renewable energy sources, the increase in number of electric vehicles and the emergence of novel stakeholders such as prosumers, the European energy system is currently undergoing significant transformation. The picture below sketches how urban distribution systems will look in the future, containing both traditional consumers, renewable generation, and charging stations.
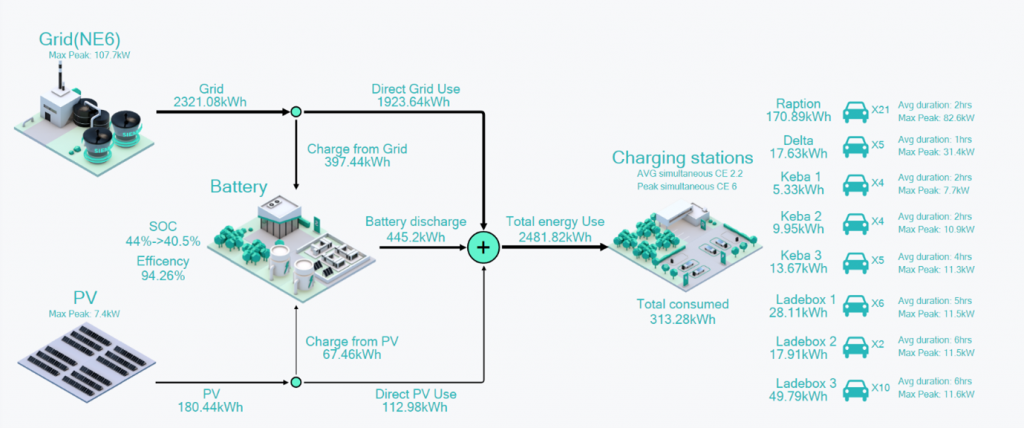
This transition has created new business models such as energy storage solutions and demand-side management services and energy communities, which are actively transforming the ways energy is produced, distributed, and consumed.
As energy systems become more decentralized and diverse, their complexity increases significantly. With so many new stakeholders and technologies being integrated into the energy mix, it can be challenging to track and analyze the many and diverse factors impacting the system’s performance and their underlying root causes. Furthermore, with the appearance of different actors there is a need to explain system-related events and changes to stakeholders.
This makes the smart grid an ideal use-case for applying and demonstrating the technologies developed within SENSE, namely to:
- (i) identify unusual events occurring in the context of electrical vehicle charging and local energy communities;
- (ii) derive the root causes of these events; and
- (iii) derive appropriate explanations for different stakeholders such as customers, system technicians, and system operators.
The use-case demonstration will be carried out in cooperation with ASCR smart city research using the smart grid testbed in Aspern, Vienna, which is Austria’s largest living lab. Additionally, prior to their application in real-life settings, the SENSE technologies will be tested on various scenarios represented within the BIFROST smart grid simulation engine.
